India's financial system is a complex and dynamic network that drives economic growth. From the bustling stock markets to the intricate web of banking institutions, understanding how this system operates is crucial, not just for financial professionals but for anyone keen to grasp the nation's economic heartbeat.
The Financial Backbone of India
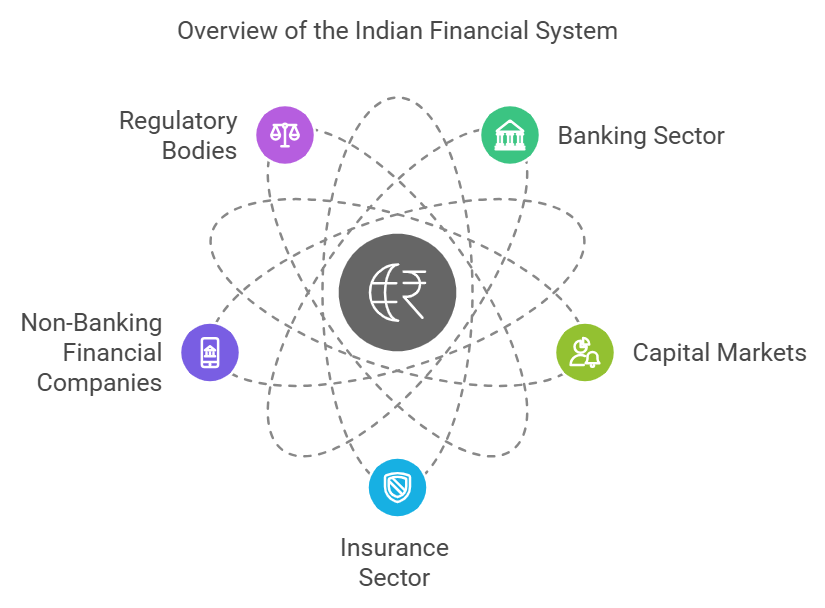
At its core, the Indian financial system comprises various institutions, markets, and instruments. Here are some key components:
-
Banking Sector
Commercial banks, cooperative banks, and regional rural banks form the backbone of banking and the Indian financial system. The banking system facilitates the flow of funds from savers to borrowers while ensuring liquidity and stability.
-
Capital Markets
These include stock exchanges like BSE and NSE, where shares and securities are traded. A well-functioning capital market is integral to the Indian finance management system, driving investments and economic growth.
-
Insurance Sector
Insurance companies offer protection against financial loss. The two main categories are life insurance and general insurance, which contribute to the overall stability of the system.
-
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
These entities provide financial services like loans, retirement planning, and asset management but do not hold a banking license. Their role has grown significantly in recent years.
-
Regulatory Bodies
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), and the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) ensure stability and oversee the functioning of the system.
The Indian Financial Ecosystem
The Indian financial system operates within a global context. International trade, foreign exchange markets, and foreign direct investment (FDI) significantly impact the Indian banking and financial system. For instance, fluctuations in foreign exchange rates can influence import-export dynamics, affecting domestic liquidity and market trends.
Financial Instruments in the Indian Financial System
A wide array of financial instruments ensures smooth operation:
-
Treasury Bills
Used by the government to manage short-term liquidity.
-
Commercial Papers
Issued by corporations to finance their short-term obligations.
-
Certificates of Deposit
Offered by banks as a low-risk investment option.
These instruments are essential for managing cash flow and supporting economic activities.
Functions of the Indian Financial System
The Indian financial system plays an important role in the economy:
-
Mobilizing Savings
It encourages individuals and businesses to save and invest.
-
Facilitating Payments
Ensures smooth transactions between entities.
-
Providing Liquidity
Offers mechanisms to convert assets into cash when needed.
-
Promoting Economic Growth
By allocating resources efficiently and enabling investments.
Challenges and Opportunities
The system also faces challenges like financial inclusion, inflation control, and managing non-performing assets (NPAs). However, advancements in digital banking and fintech integration present opportunities to overcome these hurdles. Recent developments, such as the Goods and Services Tax (GST), have further streamlined financial operations and enhanced transparency.
Role of Global Financial Integration
Global financial integration has deepened the connections between domestic and international markets. Policies governing foreign direct investment (FDI) and foreign institutional investment (FII) influence capital inflow, while international agreements shape trade policies. India's economy relies heavily on maintaining a robust financial ecosystem that can adapt to global trends.
Online M.Com & M.A. Economics Programs at Andhra University
If you're passionate about understanding the nuances of the Indian financial system, Andhra University's online M.Com and M.A. Economics online degree programs provide an excellent opportunity. These programs equip students with practical knowledge of finance and economics, preparing them for dynamic careers in these fields.
Conclusion
The Indian financial system is a captivating labyrinth of institutions, markets, and regulations. From understanding the role of regulatory bodies to exploring financial instruments, this system provides insights into the nation's economic heartbeat.
Whether you're aspiring to build a career in finance or economics or simply curious about how the economy operates, exploring the intricacies of the Indian finance management system can empower you to make informed decisions and contribute to India's growth.So, take that step into the world of finance, a world rich with opportunities waiting to be explored.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The Indian financial system consists of financial institutions (banks, NBFCs), financial markets (capital and money markets), financial instruments (treasury bills, bonds, commercial papers), and regulatory bodies like RBI, SEBI, and IRDAI. These components collectively ensure the smooth functioning of the economy by mobilizing savings, facilitating investments, providing liquidity, and regulating financial operations. Their importance lies in maintaining economic stability and fostering growth.
The Indian financial system mobilizes savings from individuals and institutions and channels them into productive investments like infrastructure, industries, and services. It ensures efficient allocation of resources, facilitates payments, and provides liquidity for businesses and individuals. By connecting savers and investors, it supports capital formation, employment generation, and innovation, which are vital for the country’s economic growth.
The Indian financial system faces challenges such as limited financial inclusion, increasing non-performing assets (NPAs) in the banking sector, inflationary pressures, and adapting to rapid technological advancements. Efforts like promoting digital banking, implementing financial literacy programs, introducing regulatory reforms, and encouraging fintech adoption aim to address these challenges. Government initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana and reforms such as GST have also contributed to streamlining the system.
Courses like Online M.Com and M.A. Economics Online provide an in-depth understanding of the Indian financial system’s intricacies, including its components, challenges, and global integration. They equip students with practical knowledge of financial management, economic policies, and market trends. Such programs prepare you for careers in banking, finance, and policy-making, enabling you to make informed decisions and contribute meaningfully to the economy.


